Conveniently located to serve Newnan, Peachtree City and LaGrange
Click here to jump to:
Newnan Actinic Keratosis
WHAT ARE ACTINIC KERATOSIS?
Actinic Keratosis (AKs) are precancerous skin lesions seen in on sundamaged skin. They are caused by cumulative exposure to ultraviolet radiation. AKs are also referred to by the term “solar keratosis.”
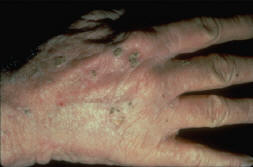
Actinic Keratosis on the hands
WHY ARE ACTINIC KERATOSIS WORRISOME?
AKs may develop into squamous cell cancer (SCC) and have been associated with basal cell cancer (BCC) lesions. AKs may develop as early as the third and fourth decade of life. Untreated lesions have up to 20 % risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Individuals who are fair skinned, have blue eyes or red or blond hair, or are outdoors much of the time are particularly susceptible to SCC development. Patients who are organ transplant patients have a significantly higher risk of developing AKs which transform into skin cancer.
WHAT DO ACTINIC KERATOSIS LOOK LIKE?
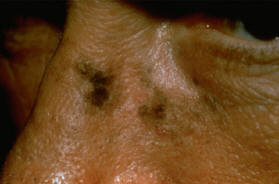
Actinic Keratosis, pigmented subtype
AKs are scaly sandpaper like lesions which can be painful or itchy. They can be categorized into four types of lesions:
- hypertrophic subtype
- pigmented subtype
- atrophic subtype
- lichenoid subtype
Often, our patients note that AKs “come and go in the same location”, are easily palpable, and have some type of discomfort, whether it be itching, tingling or burning.
Related
Content
Patient
Review
“Great staff and nice atmosphere. Everyone is professional and very attentive. You will not be disappointed.”
by T
WHERE DO ACTINIC KERATOSIS FORM AND WHERE ON THE SKIN ARE THEY MOST DANGEROUS?
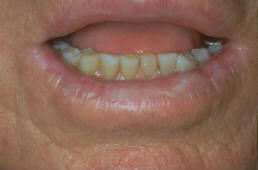
AKs on lower lip (Actinic Cheilitis)
AKs can form anywhere on the body. They usually form in sun exposed areas such as the face, scalp, and hands. They are most dangerous when they form over the lip or ear regions, as these areas are more susceptible to invasive cancer formation. If you notice recurrent AKs forming on your skin after they have been treated, you should follow-up with us for a re-evaluation and possibly a skin biopsy.
WHAT ARE SOME OF THE TREATMENTS AVAILABLE FOR ACTINIC KERATOSIS?
We often utilize a liquid nitrogen spray to treat AKs. This causes a slight blistering effect on the skin, and through causing inflammation will rid the skin of the actinic keratosis. For, the lip area (areas of high risk), the best treatment uses diclofenac (Solaraze gel). Other treatments with imiquimod have been used.This creates a local immune response after 4 weeks of therapy. Two to three treatment sessions are sometimes performed every few months.
Finally, for those patients with a multitude of lesions (where the number of AKs makes either liquid nitrogen a poor choice), Photodynamic therapy using a blue light, 5-fluorouracil cream (Carac™), or a new treatment using a chemical called ingenol mebutate has been used. CO2 laser has also been effective for treating these growths
HOW DOES ONE PREVENT AKs FROM FORMING?
Preventive measures recommended for actinic keratosis are similar to those for skin cancer prevention:
- Not staying in the sun for long periods of time without protection (e.g., sunscreen, clothing, hats).
- Frequently applying powerful sunscreens with SPF ratings greater than 30 and that also block both UVA and UVB light.
- Wearing sun protective clothing such as hats, long-sleeved shirts, long skirts, or trousers.
- Avoiding sun exposure during noon hours is very helpful because ultraviolet light is the most powerful at that time.
SUMMARY
In summary, AKs are premalignant skin growths that can develop into SCC in up to 20% of cases. To schedule an appointment for actinic keratosis evaluation and treatment, click here.